Vodafone has managed to save €500m (euros) in operating and capital expenditures (OPEX and CAPEX) over the past 3 years. In an interview article posted on TelecomTV, Vodafone CTO Scott Petty highlighted the reason for such impact due to the investment in in-house software engineering capabilities. Currently, 11000 software resources are contributing to digitalization, and looking to add more than 7000 by 2025.
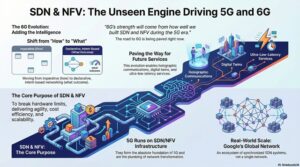
This is a prime example of how telco operators are transforming to become digital services providers rather than just network connectivity providers. This story highlights the outcome of the key initiatives taken by leading Tier 1 operators to replace network components with software representations (virtualized and containerized).
Still, we are yet to realize more such success stories from operators. Saving CAPEX and OPEX is one of the achievements but deploying 5G-driven innovative services and generating revenue is the core target for telco operators. Almost 80% of deployments are not true 5G i.e. 5G Non-standalone. When we say 5G and its services, it refers to 5G Standalone.
Not all telco operators have shifted to a 3GPP-compatible 5G Standalone (SA) core network. According to GSA, only 38 out of 515 operators globally have achieved the 5G SA in a public network that is end-to-end, software-based, and ready to support more 5G services keeping the cost in control. 5G SA core-ready public network deployments are 42 as per Counterpoint research.
The focus of the telco operators for the transformation of the existing network into a 5G network was
- Investments in OSS/BSS transformation/cloudification to quickly start generating revenues from use cases eMBB and Fixed Wireless Access at the initial level and move towards enabling support for machine-type communication (MMTC) and ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC). 5 years back, TM Forum concluded with a report that 72% of enabling and service creation revenue is dependent on OSS/BSS transformation.
- Strategies and optimize network operations and processes to control the cost (CAPEX and OPEX). Saving is equal to earning.
Cost saving by Vodafone is one case and surely there will be more such stories. But the key takeaways from this story are below
- Telcos are looking for in-house software engineering capabilities or getting into more collaborations for quick development of network core and business platforms.
- They have increased focus on cloud-native architecture practices at each layer in 5G networks i.e. core to RAN.
- CI/CD approach has played a significant till now. But now, it is time to utilize machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate and efficiently manage most of the network operations.
- Quick services roll-out within a network is slowly becoming a focus as telcos are looking to target the enterprise segment with promised innovative 5G services (Drones, AR/VR, gaming, etc).
We can say that telco operators can see eMBB and FWA use cases in sight with T Mobile’s success. This year, telco operators will be more aggressive toward the 5G SA network which will help them to tap revenue opportunities from MMTC & URLLC-based use cases.
Appledore research’s consulting analyst Rahul Atri emphasized on selling use cases can be a quick revenue generation opportunity in a recent 5G Monetization Forum event. But telco operators must make sure that they cannot achieve a stage of selling innovative use cases without a 5G SA core.
At this point, realizing automation was the initial key, and applying AI/ML in the network is considered to be the next phase after that. In 2023, It will be interesting to see how other Tier 1 and mostly Tier 2 operators and connectivity providers leverage learnings from this and plan their way ahead to generate new revenue streams.



Be First to Comment