5G technology represents a significant leap forward for humanity, offering faster connectivity and the potential to revolutionize various industries. One of the sectors poised to benefit from 5G is aviation. As 5G use cases have started emerging across industries, the aviation sector is also set to undergo transformative changes due to the benefits of 5G connectivity. However, the road to 5G integration in aviation has not been without its challenges, particularly concerning potential interference with critical aircraft systems.
Why is 5G Important for Aviation?
Simply put, 5G enhances connectivity speeds by over ten times compared to 4G networks. According to a GSMA report, 5G has already reached 1.5 billion subscribers by the end of 2023, and this number continues to grow. The appeal of 5G lies in its ability to support a wide array of IoT and digital use cases, driving the next wave of technological disruption, likely powered by AI.
In the aviation industry, 5G can be leveraged in several areas:
- In-flight connectivity: Faster and more reliable internet for passengers.
- Airport operations: Streamlining processes such as baggage handling and security checks.
- Predictive maintenance: Using 5G-powered IoT devices to monitor and predict equipment failures.
- Remote air traffic control: Enhancing the efficiency and safety of air traffic management.
- Inventory and supply chain management: Improving accuracy and speed through real-time data collection.
As 5G matures in aviation, augmented and virtual reality could offer passengers immersive experiences, such as virtual tours of the aircraft or personalized in-flight entertainment.
The 5G Interference Issue: What’s the Concern?
One of the primary concerns surrounding 5G in aviation is the potential interference between 5G signals and radio altimeters used in aircraft. Radio altimeters are crucial for determining an aircraft’s height above the ground, especially during landing in low visibility conditions. These altimeters operate within the 4.2-4.4 GHz frequency band, while 5G networks use the C-band spectrum at frequencies between 3.7 and 3.98 GHz. Although there is a small gap (0.22-0.24) between these frequencies, there have been reports of pilots receiving erroneous ground proximity warnings due to potential 5G signal interference. This interference could also disrupt other systems reliant on altimeter readings, such as the Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) and terrain awareness systems, posing significant risks to flight safety.
Lessons from Tel Aviv: A Case Study
A notable incident occurred during military operations near Tel Aviv airport, where several radar altimeter interference events led to inappropriate terrain warnings and erroneous autopilot activations at low altitudes. Without timely pilot intervention, these events could have resulted in catastrophic outcomes, such as stalls and loss of the aircraft. This case underscores the critical importance of addressing the 5G interference issue to ensure aviation safety.
Mitigating the Risk: The Role of Regulatory Bodies
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has taken the lead in ensuring the safe integration of 5G technology without compromising aircraft safety systems. The FAA has worked closely with telecom companies and the aviation industry to establish guidelines and mitigate potential interference risks. Significant milestones have been achieved, including agreements with AT&T and Verizon to delay some C-band and 5G usage, upgrading airplane altimeters, and setting deadlines for the aviation industry to adapt to these changes.
Here’s how the FAA has demonstrated mitigation efforts for signal interferences.
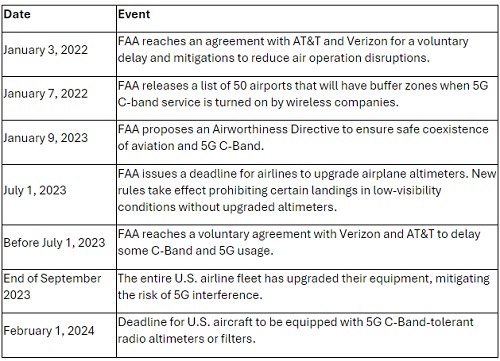
Similarly, international aviation stakeholders, including the National Business Aviation Association (NBAA), International Air Transport Association (IATA) and Transport Canada, have been actively engaged in finding suitable mitigations to enable 5G networks to coexist safely with critical aviation systems.
In India, telecom operators are deploying in-building solutions (IBS) at airports to enhance 5G coverage. Fortunately, the spectrum allocated for 5G services in India is not close to the altimeter spectrum, allowing operators to deploy these solutions without significant interference concerns.
What’s Next for Aviation with 5G?
The future of aviation with 5G holds exciting possibilities:
- Higher Speeds and Lower Latency: 5G networks offer peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, drastically reducing the time required for data transfers, such as downloading applications or streaming content during flights.
- Enhanced Security and Efficiency: Airports can deploy advanced security measures, including 4K/8K cameras and facial recognition technology, to streamline passenger processing and improve safety.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: Airlines can engage passengers with immersive experiences, such as virtual tours of the aircraft or interactive advertising.
- IoT Integration: 5G enables the use of automated vehicles and robots within airports, enhancing operational efficiency and passenger convenience.
As we look to the future, integrating 5G into the aviation industry brings both great opportunities and some challenges. While 5G can vastly improve connectivity, operations, and passenger experiences, we must also be mindful of the potential risks, especially regarding signal interference with aircraft systems.
To make the most of 5G, industry leaders need to continue working closely with regulators, telecom companies, and tech innovators. The focus should be on creating strong safety measures, improving the reliability of crucial aviation systems, and ensuring everyone involved is on the same page.
We’re just at the beginning of bringing 5G into aviation. With careful planning, smart investments, and a strong commitment to safety, the industry can reach new heights, making air travel not only better but also safer and more efficient in the years to come.




Be First to Comment